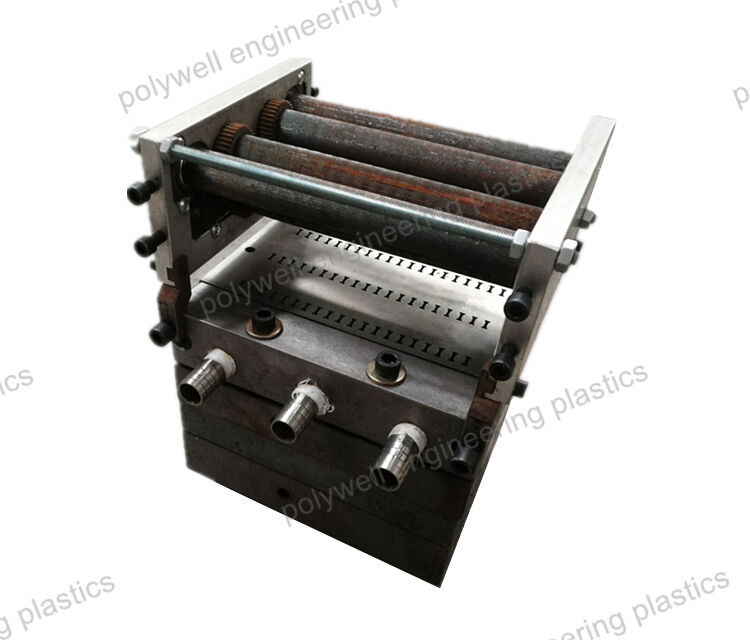
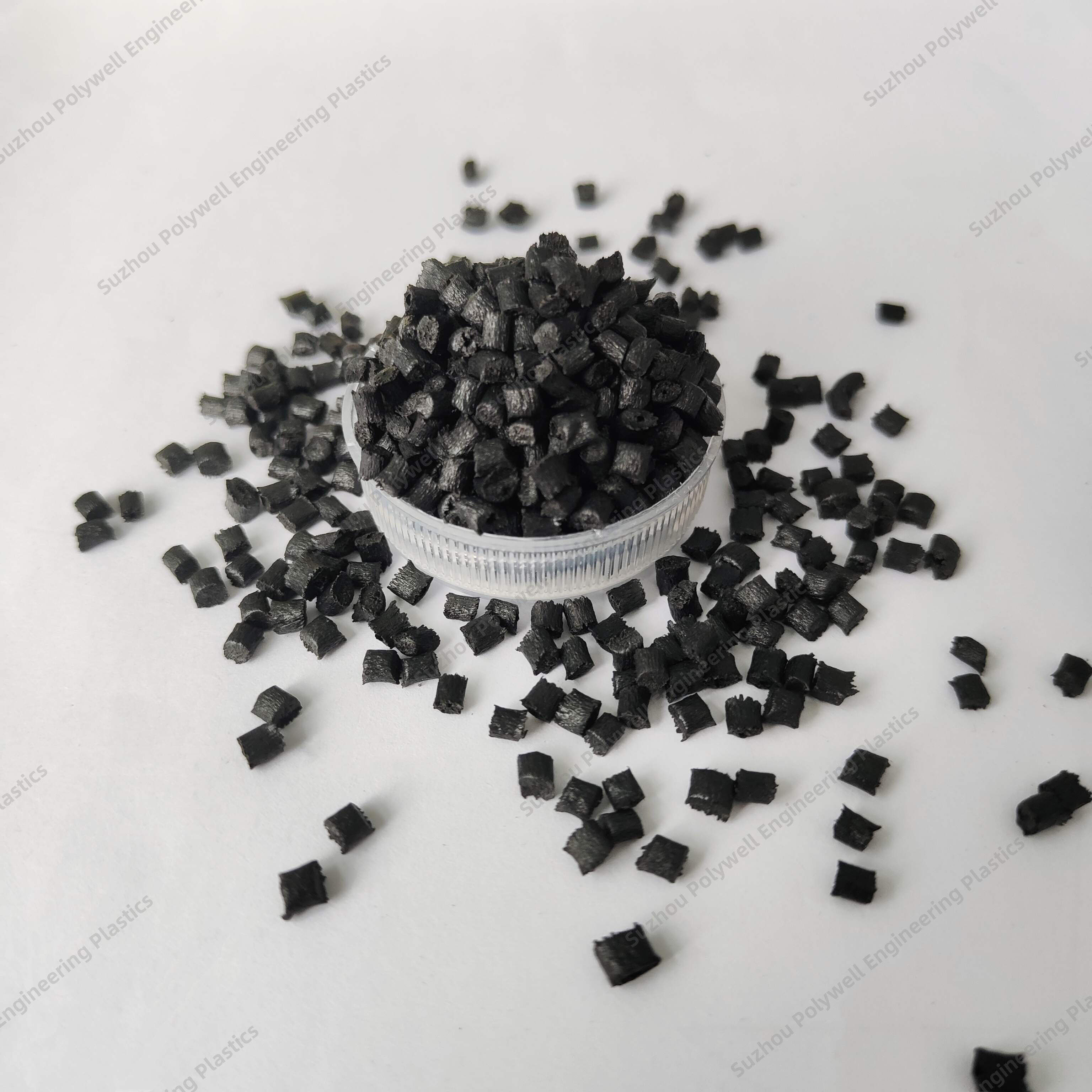
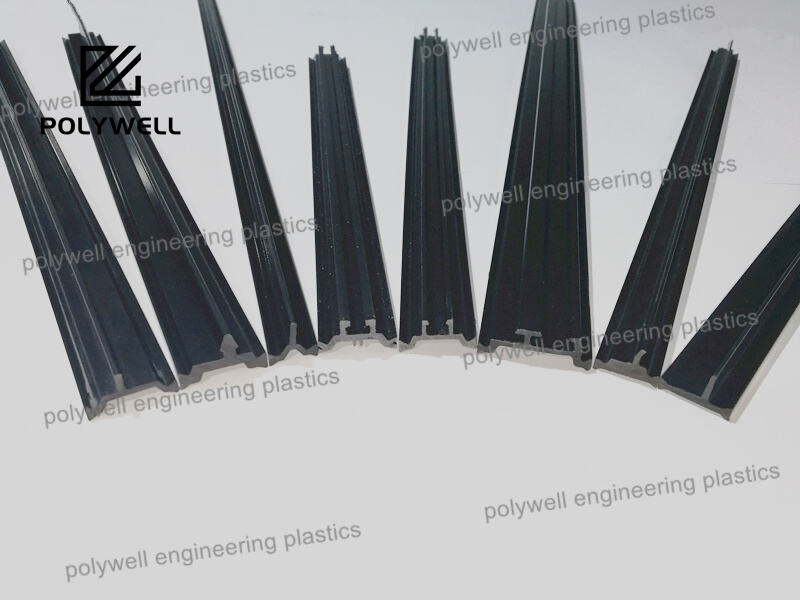
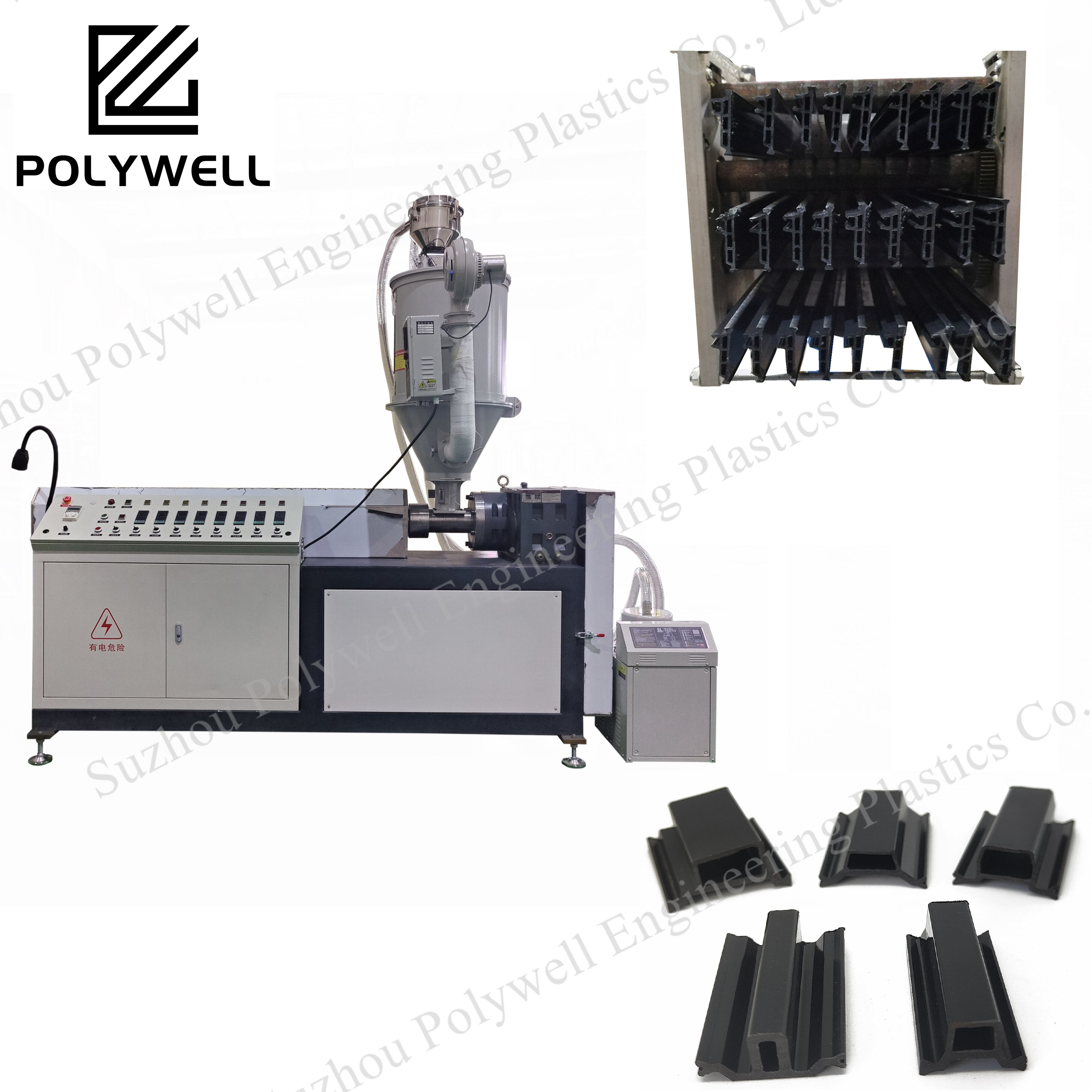
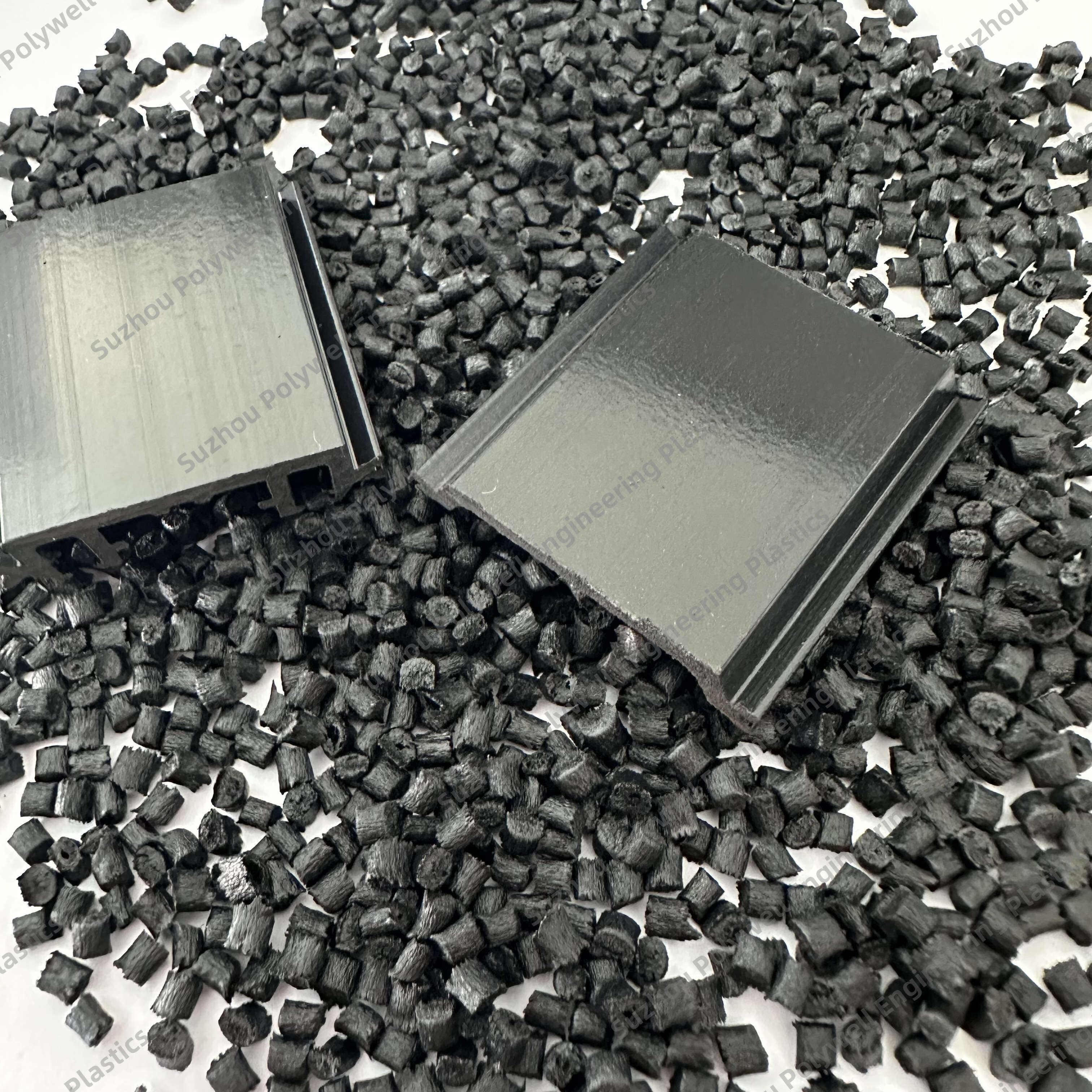
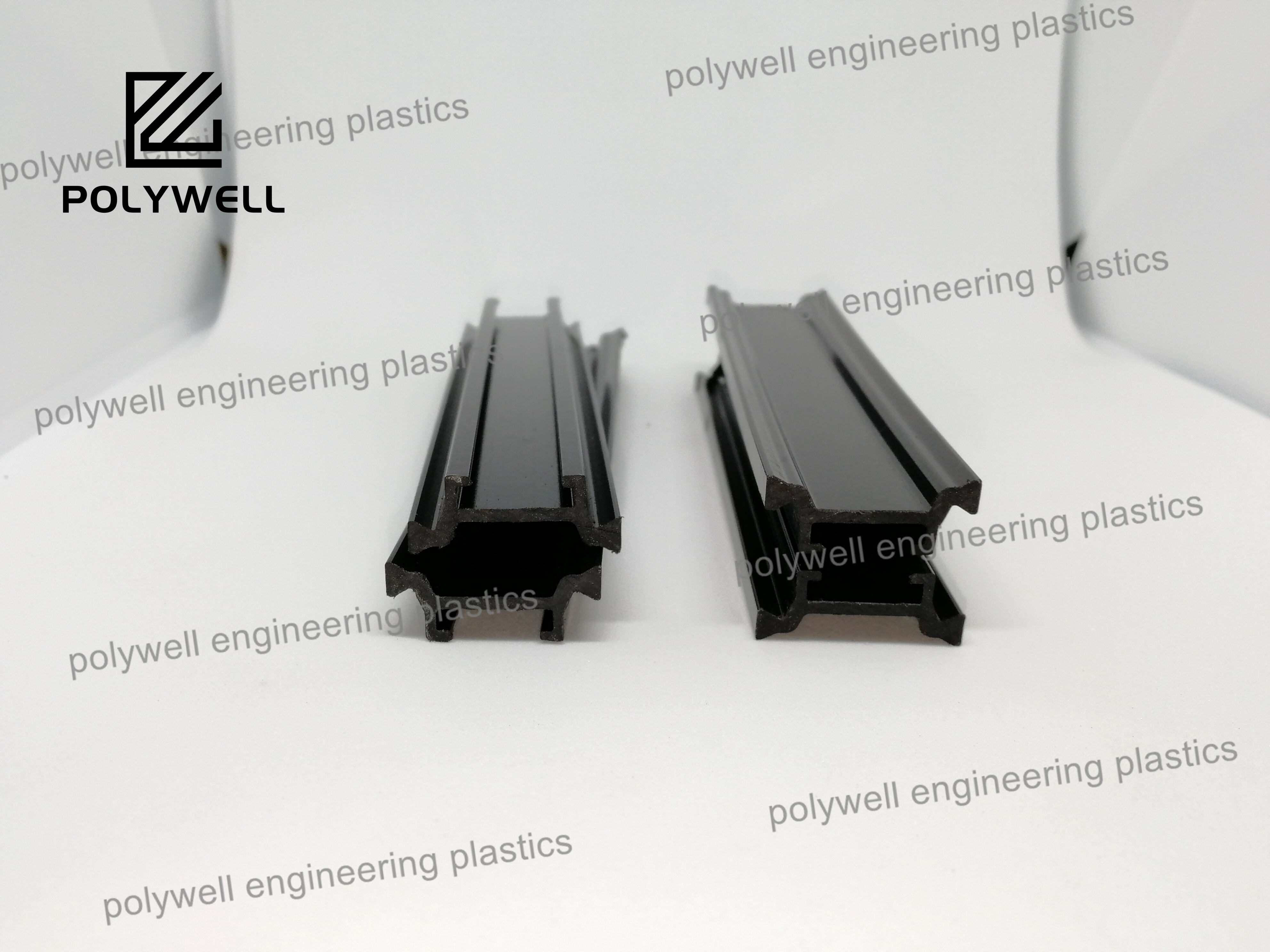
25% Glass Fiber Reinforced Polyamide PA66 Thermal Break Strip for Heat Break Aluminum System Window and Door
Surface Finishing:Unfinished
Application: Thermal break aluminum profiles / Heat Insulation aluminum frame / Thermal broken bridge aluminum window
Raw material: PA66GF25 granules / polyamide 66 reinforced by fiberglass / Nylon66-gf25 pellets
Technical Performance: GB/T236151.1-2009 / GB/T236151.1-2017
Print: Customized laser printing
UV resistance: Yes
HS code: 391690
Port: Shanghai Port
Size: As drawing
Length: 6m/piece or customized
OEM service: available
- Overview
- Related Products
What is a thermal break strip?
Thermal break strip, also called heat insulation strip, is a part of aluminum bridge profile. The heat-insulating bridge aluminum-plastic profile can realize the three-way sealing structure of doors and windows, and reasonably separate the water vapor chamber. It successfully realizes the pressure equalization of gas and water, and significantly improves the watertightness and airtightness of the doors and windows.
Insulation of aluminum doors and windows sealed with insulation strip is the one with the glass fiber reinforced polyamide nylon (PA66), referred to as Nylon 66 insulation strips, expansion coefficient is small, heat-resistant, and anti-aging properties.
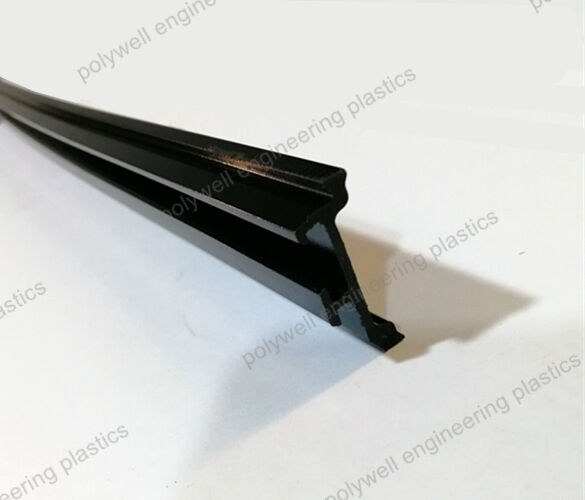
High Precision For Aluminum Sash Window Frame PA66 25% Fiberglass Thermal Insulation barrier strips.
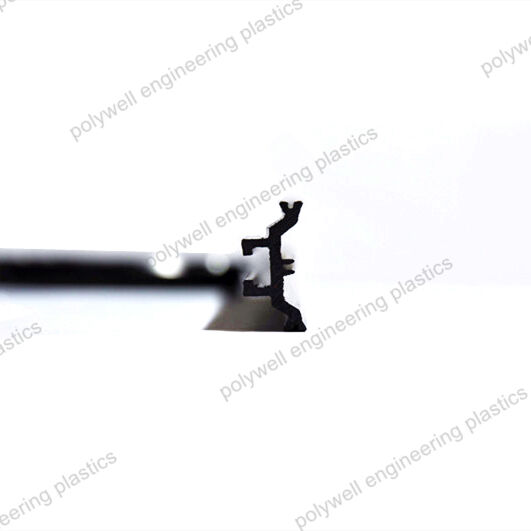
Inserted in the thermal break aluminium profiles, and being the part of energy-saving window system for reducing heat conduction.
The shape I polyamide thermal barrier material can prevent the window frame from dust and water and could realize a better Uf value by sealing with a rubber profile, mostly used on the sash.
Can polyamide strips thermally break aluminum extrusion assemblies?
Yes.
Structural insulating polyamide strips have been utilized for thermally breaking aluminum extrusion assemblies for over 30 years and have been in use in north america for over a decade. Polyamide strips are available with many configurations to meet different performance specifications. Creating a thermal break utilizing a polyamide strip system entails a 3 step process.
1. Profile knurling
2. Strip insertion
3. Crimping

What are the different types of thermal barriers?
Currently, there are two principal types of thermal barriers: polyamide thermal barrier strip and pour & debridge (P&D).
Our company only produce polyamide thermal barrier strip.
The Function of Thermal Break Strips in Window
Broken bridge heat-insulated aluminum alloy doors and windows is to divide the original whole-body aluminum alloy profile into two on the basis of traditional aluminum alloy doors and windows. The overall heat-insulating profile enables the heat-insulating strip and the aluminum alloy to jointly bear the load caused by the glass's own weight, wind pressure and temperature stress. Therefore, the use nature of the heat insulation strip determines that it must have high strength and excellent stability at the same time, otherwise it will easily cause doors, windows and curtain walls to break and fall off, causing major quality and safety hazards.
The word "bridge" in the name "broken bridge aluminum" means "hot and cold bridge" in material science, and the word "broken" stands for action words, which means "cut off the hot and cold bridge". Specifically speaking, aluminum alloy is a metal medium with strong thermal conductivity. When it collides with the temperature outside the house by a large difference, the aluminum alloy becomes a "bridge" for heat transfer. Using this type of material to make doors and windows, it will have Poor insulation too. However, the broken bridge aluminum is to disconnect the aluminum alloy from the middle, and the thermal conductivity of the plastic will be weaker than that of the metal. The disconnected aluminum alloy is connected together with hard plastic, so that the heat will not easily flow to the whole. material, so the heat insulation will become better, which is the origin of the name "broken bridge aluminum (alloy)".

What is a Thermal Barrier?
Thermal barriers are made from resins that create a “thermal break” between the inner and outer surfaces of aluminum fenestration.
Thermal barriers reduce heat loss or heat gain through the aluminum.
Thermal barriers improve the U-value characteristics of finished systems.
Thermal barriers are about energy conservation, U-values and government codes.
70 percent of aluminum fenestration systems produced in North America contain a thermal break.
Primarily used in colder climates to reduce heat loss.
Increasing use of thermal barriers to reduce heat gain and also reduce heat loss.
Developers, architects and designers are demanding better performance in terms of power usage.
Stricter government regulations to reduce power usage in buildings to combat environmental concerns.
Aluminum, if it is to retain its market superiority in terms of its structural integrity, will have to achieve better performance in terms of U-values.
The use of thermal barriers will assist manufacturers to achieve improved LEED performance.
Advantages of polyamide strips
The polyamide strip is a material of low thermal conductivity which will minimise the transfer of heat and cold through the window frame, resulting in improved energy efficiency. The polyamide strip will have a HUGE impact in reducing transfer of heat and cold over typical non-thermal profiles. These sections can be anodized or powder coated to withstand the harsh climate, including UV damage and salt corrosion.
The wider the thermal break, the greater insulation performance.
Thermally Broken windows are a major contribution to sustainable and eco-friendly homes. They help to save money, energy and support the environment.
Application
Polyamide strip is one of the most common materials used for years to create thermal breaks in curtain walls, commercial windows, doors, and more. It is installed between the interior and exterior profiles of the windows that forms an insulating barrier between the two.

Characteristic of PA strips
According to different storage time and ambient climate, the dimension of PA strips will increase slightly because of the natural moisture absorption. And the mechanical properties will change slightly too.
So, PA strips should be transported and stored under dry conditions away from the influence of weather. (rain, direct sunlight etc.)
What is the Suitable Width for Thermal Break Strips in Windows?
Generally speaking, the wider the heat insulation strip, the better. Under the premise of no damage to the product and the stability and quality of the heat insulation strip, the wider the aluminum insulation strip, the better, because the wider the heat insulation strip, the less heat transfer. The slower the window is, the better the insulation performance of the window is, and the more energy-saving it is, but the insulation strip must use PA66GF25 nylon strip.
On the contrary, if there is no quality assurance of aluminum material, poor or damaged heat insulation strips, and the toughness of the product is not up to standard, it is recommended not to choose windows with too wide heat insulation strips, because the overall airtight system is a whole system , everything has a standard, and the one that fits the standard is the best. If the heat insulation strip is narrow, the heat insulation will be worse. If the heat insulation strip is wide, it will affect the doors and windows. Other materials will be less. The load-bearing strength of the doors and windows will be reduced.
Take 70 broken bridge aluminum doors and windows as an example: the standard width of the window insulation strip is between 2 cm and 2.5 cm, and it should not be too wide or too narrow; if it is 80 series or 90 series broken bridge aluminum doors and windows, wider insulation strips can be used. For heat strips, it is recommended that if the heat insulation strip exceeds 4 cm, it is better to choose imported brand heat insulation strips or brand heat insulation strips produced by domestic large-scale heat insulation strip factories.
When the width of the heat insulation strip reaches more than 40mm, the stability of the system will become worse, and with the increase of the cavity between the heat insulation strips, the loss of heat due to the convection effect will become more and more obvious, so the wider the heat insulation strip, The material composition and design of the heat insulation strip are obviously different from the conventional heat insulation strips. The wider heat insulation strips should use mesh heat insulation strips or spacer cavities in the middle, which greatly improves the stability and heat insulation and sound insulation performance of the heat insulation strips.
How to storage polyamide thermal break strips?
First, Store profiles horizontally in order to prevent bending or twisting the material, otherwise long storage periods cause permanent sagging. Support long lengths.
Second, Maintain ambient temperature in the range from 15 to 20 °C.
Third, Protecting against moisture.

Our service about test
1.Size precision inspection insulation, according to the national standard GB/T23615.1-2017, the size precision of detection for customers of heat insulation strip.
2.Detection and analysis of insulation of internal structure, according to the national standard GB/T23615.1-2017.analyze the internal structure of insulation detection for customers.
3.Insulation density test, according to the national standard GB/T23615.1-2017, the application of electronic weighing instrument for detecting insulation density.
4.According to the national standard GB/T23615.1-2017, the insulation room temperature transverse tensile characteristic value, non-notched impact strength, high temperature and transverse tensile characteristic value of the test.
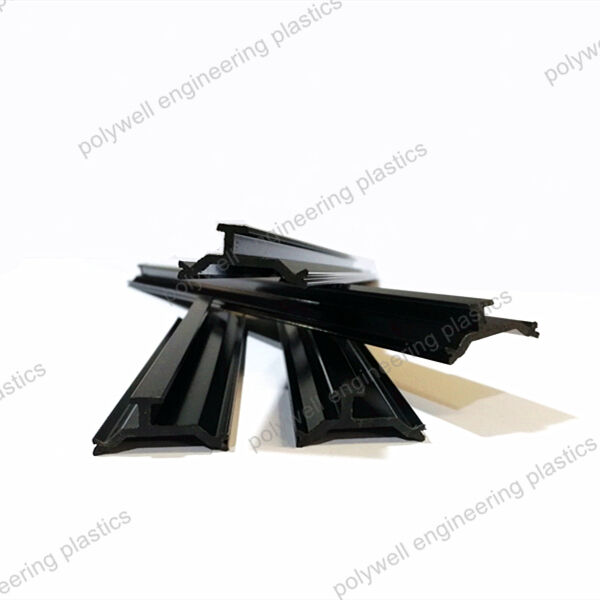
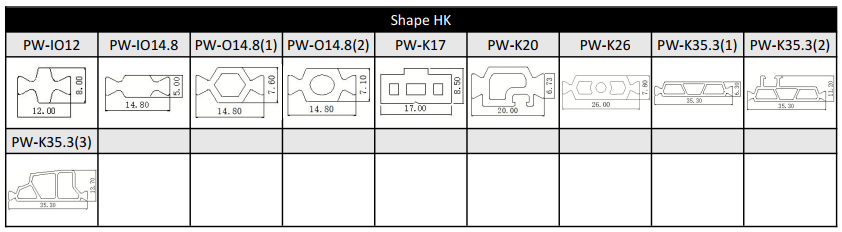
Different shapes:
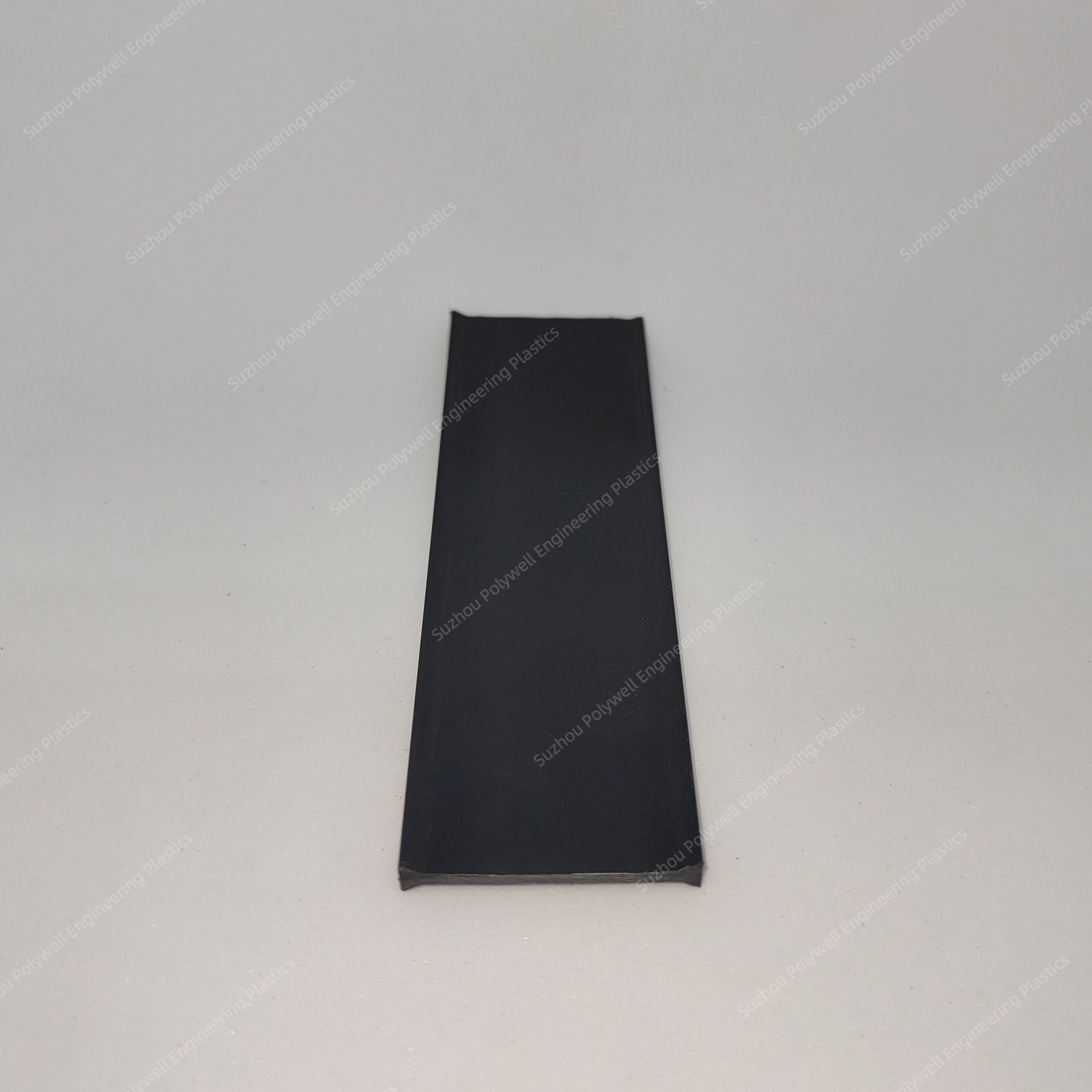
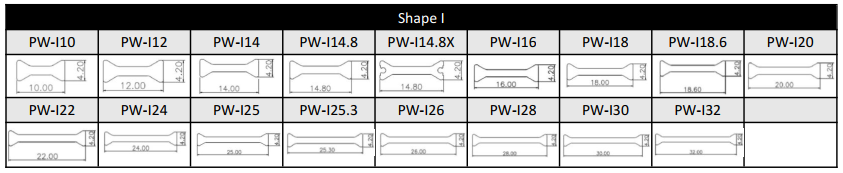
I-type thermal break strip is a common insulation material for doors and windows, with a shape similar to the uppercase English letter "I". It is the first generation and easiest shape of polyamide strips.
Compared to other types of thermal break strips, the advantage of I-type strips is that their longer length can better adapt to the width of doors and windows, improving the thermal break effect.
In addition, Type I insulation strips can also adapt to different door and window sizes and specifications through their own shape and structure, with high flexibility and adaptability.
For the I-type strips, we can provide the following size or customize according to customer’s drawing.
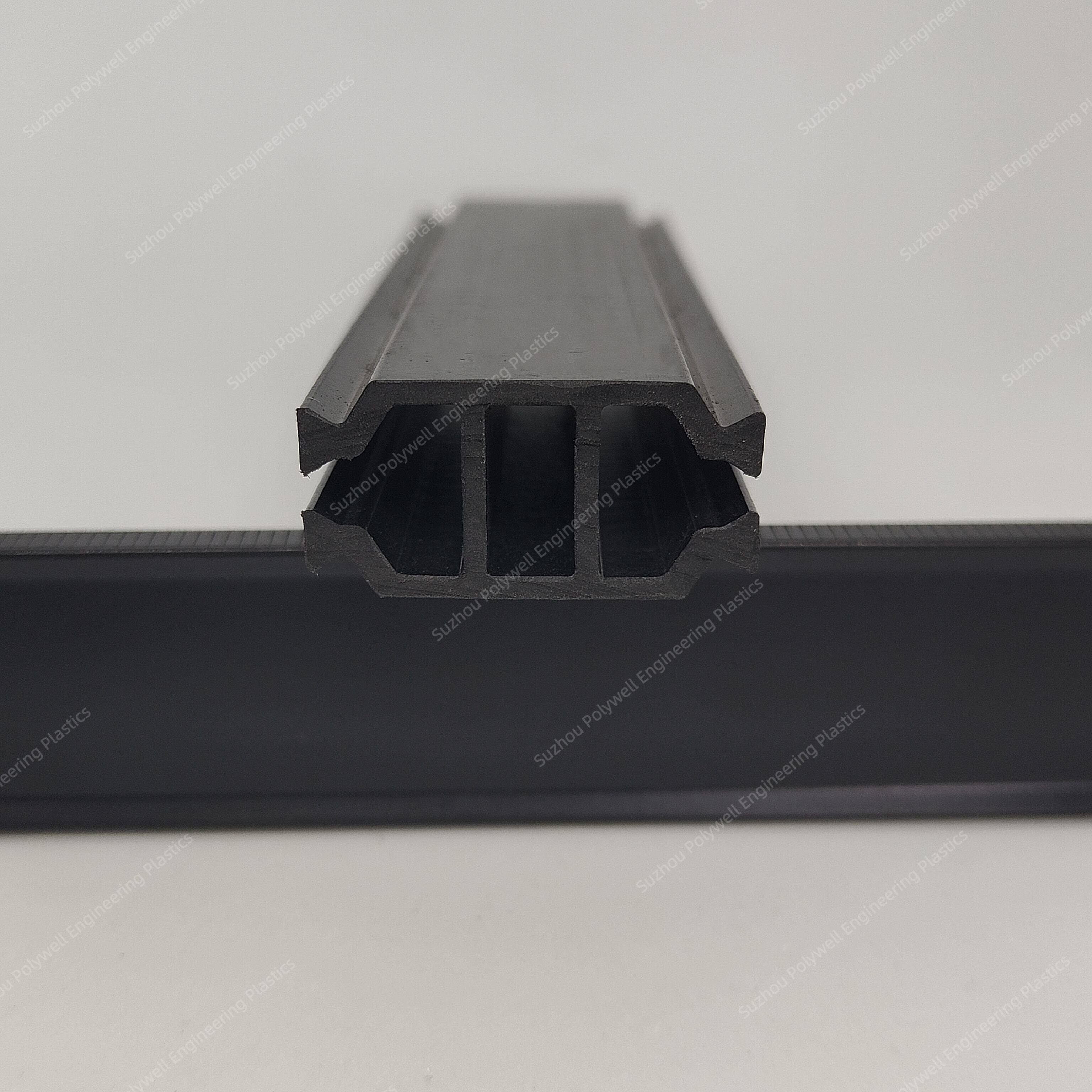
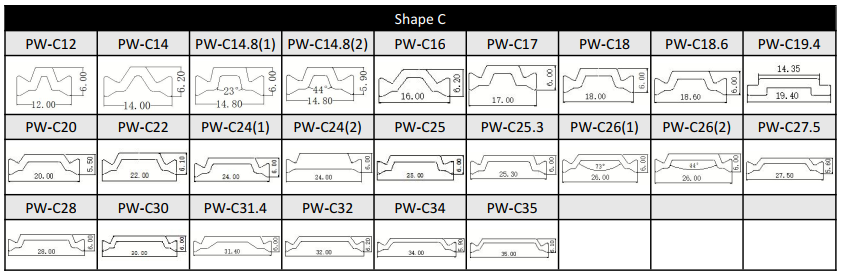
The C-type design provides a longer heat conduction path, resulting in better heat insulation performance than I-type strip, while also having better longitudinal load-bearing capacity. Besides, the C-type PA strip is also a necessary condition for the stepped drainage of thermal broken bridge aluminum.
For the C-type strip, we can provide the following size or customize according to customer's drawing.
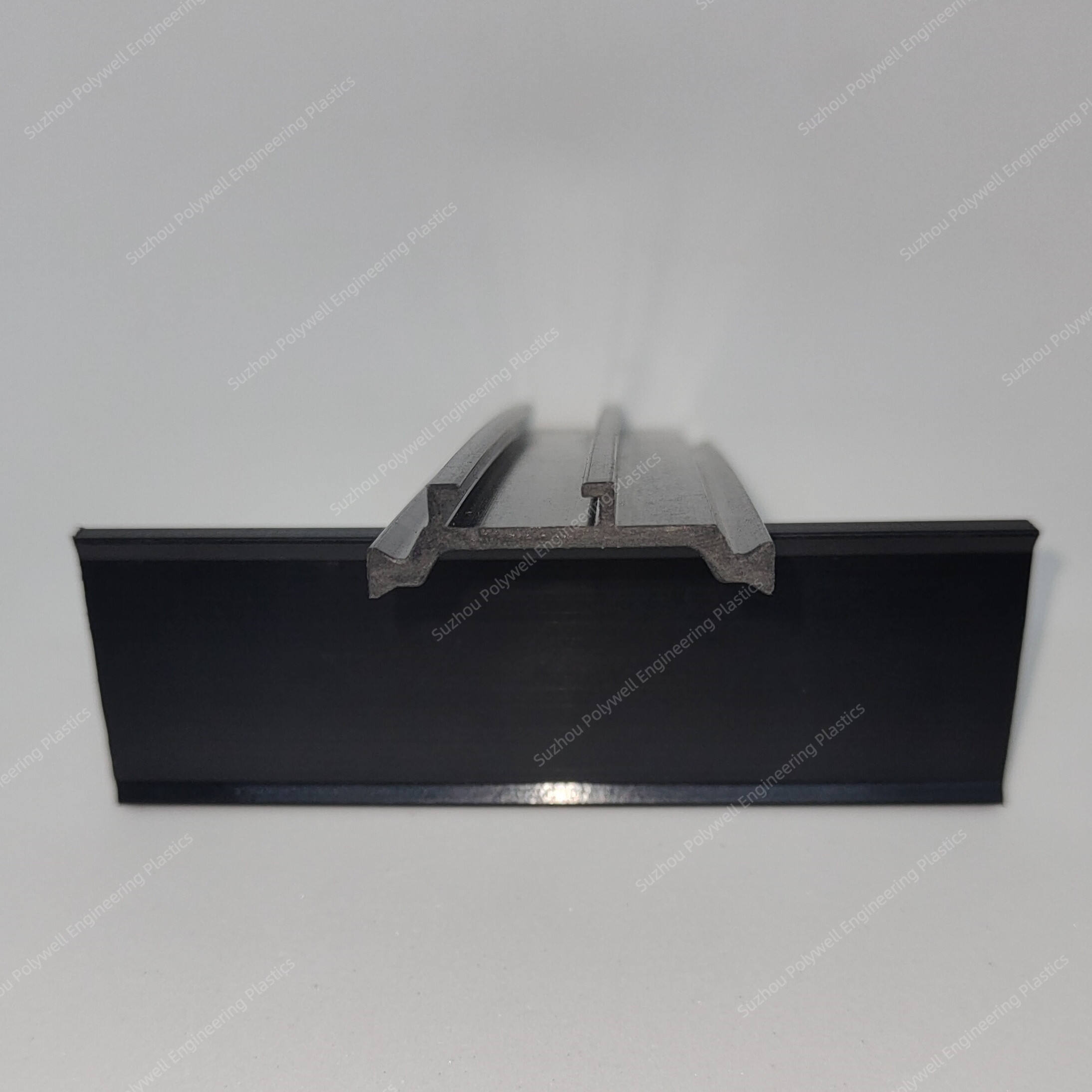
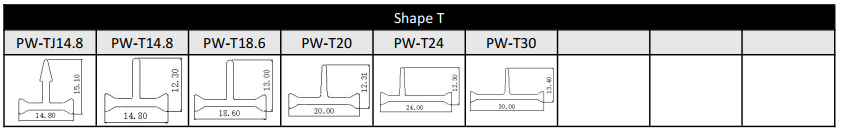
The design of T-type thermal break strips usually includes a horizontal section and a vertical section, forming a "T" - shaped structure.
This design adds a small section under the thermal break strip, allowing the sealing strip to overlap with the thermal break strips, thereby improving the overall insulation performance.
For the T-type strip, we can provide the following size or customize according to customer's drawing.
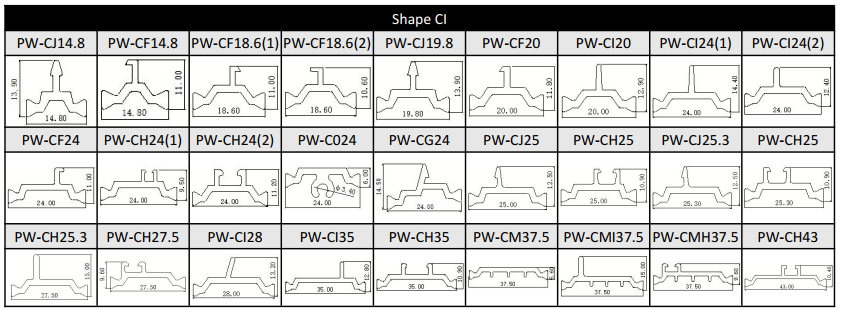
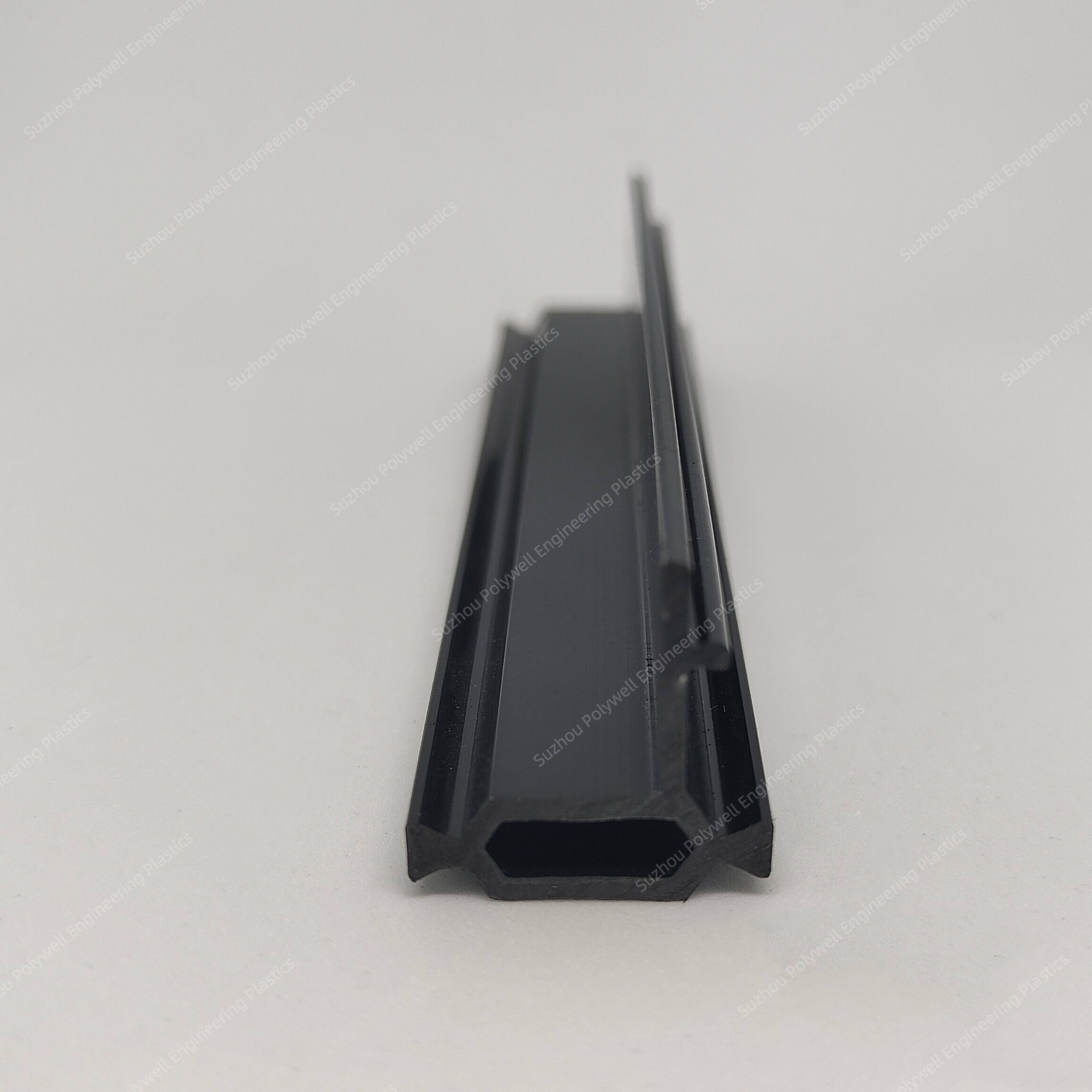
Hollow thermal break strip, also known as multi-cavity insulation strip, can reduce heat transfer by changing the air flow path, thereby achieving insulation effect and further improving insulation performance.
Hollow thermal break strip are currently the mainstream products in the market and can support large width sizes. Many thermal break strips with a diameter of 35mm or more on the market are made into multi-cavity shapes, and their longitudinal load-bearing capacity is very high.
For the hollow type strip, we can provide the following size or customize according to customer's drawing.
Product Performance
|
Item |
Unit |
GB/T 23615.1-2009 |
PW-Technical specification |
|
Density |
g/cm3 |
1.3±0.05 |
1.28-1.35 |
|
Linear expansion coefficient |
K-1 |
(2.3-3.5)×10-5 |
(2.3-3.5)×10-5 |
|
Vicat softening temperature |
ºC |
≥230 |
≥233 |
|
Melting point |
ºC |
≥240 |
≥240 |
|
Testing for tensile cracks |
- |
No cracks |
No cracks |
|
Shore hardness |
- |
80±5 |
77-85 |
|
Impact strength(Unnotched) |
KJ/m2 |
≥35 |
≥38 |
|
Tensile strength(longitudinal) |
MPa |
≥80a |
≥82a |
|
Elasticity modulus |
MPa |
≥4500 |
≥4550 |
|
Elongation at break |
% |
≥2.5 |
≥2.6 |
|
Tensile strength(transverse) |
MPa |
≥70a |
≥70a |
|
High temperature tensile strength(transverse) |
MPa |
≥45a |
≥47a |
|
Low temperature tensile strength(transverse) |
MPa |
≥80a |
≥81a |
|
Water resistance tensile strength(transverse) |
MPa |
≥35a |
≥35a |
|
Aging resistance tensile strength(transverse) |
MPa |
≥50a |
≥50a |
1. Sample water content less than 0.2% by weight.
2. Norm laboratory condition:(23±2)ºC and (50±10)% relative humidity.
3. The specifications marked with "a" only applies to I-shape strip otherwise, the specifications concluded between supplier and buyer through consultation, shall be written in contract or purchase order.

 EN
EN